Metallized Alumina Ceramic: 5 Key Points for 2025
Every year, 15-25% of high-voltage vacuum devices, power modules, and X-ray tubes worldwide face rework due to poor metallization adhesion, CTE mismatch, or hermetic leaks. As a specialized manufacturer of high-purity metallized alumina ceramics, we've distilled the 5 most essential knowledge points on metallized alumina ceramic to help engineers avoid 90% of common pitfalls and boost first-pass yield.
1. What Is Metallized Alumina Ceramic?
Metallized alumina ceramic = High-purity Al₂O₃ substrate (typically 96%-99.5% alumina) + a reliable metal layer on the surface (most commonly Mo-Mn base + Ni plating).
Pure alumina excels in hardness (>9 Mohs), insulation (>10¹⁴ Ω·cm), and corrosion resistance, but its inert surface prevents direct brazing to metals. The metallization layer acts as a "bridge," enabling hermetic ceramic-to-metal sealing (e.g., with Kovar, copper, or stainless steel) in extreme environments like vacuum, high voltage, and RF.
Quick Comparison Table (Pure vs. Metallized):
| Property | Pure Alumina Substrate | Metallized Typical Values | Real-World Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Wettability | Extremely poor | Contact angle <10° (after Ni) | Enables direct brazing |
| Thermal Conductivity | 20-30 W/m·K | Deviation <5% | Minimal impact on heat dissipation |
| Dielectric Strength | 15-20 kV/mm | Reduction <0.5% | Still excellent for high voltage |
| Hermeticity (He Leak) | None | ≤5×10⁻¹¹ Pa·m³/s | Meets ultra-high vacuum standards |
2. The Most Common Process: Mo-Mn Metallization
Over 80% of industrial applications use the Mo-Mn (molybdenum-manganese) process due to its maturity, cost-effectiveness, and strong adhesion (≥20 MPa shear strength).
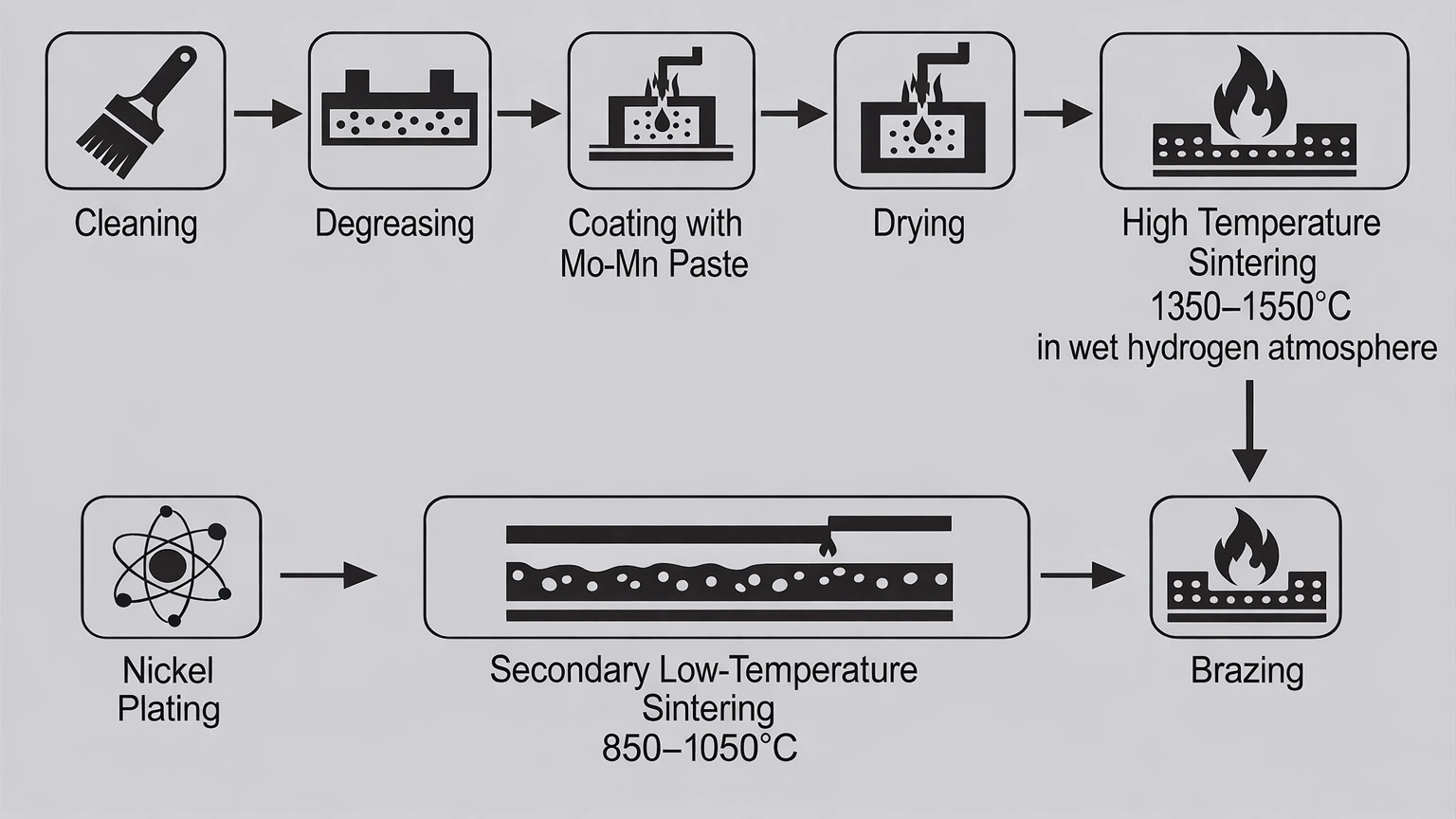
Key Process Parameters Table:
| Stage | Critical Parameter | Common Issues & Controls |
|---|---|---|
| Paste Coating | Wet thickness 80-120 μm | Uneven → localized weak adhesion |
| Sintering | 1475±10°C, O₂ <5 ppm | Excess oxygen → oxidation failure |
| Ni Plating | 7-12 μm, per MIL-G-45204 | Too thin → poor wetting; too thick → stress |
Compared to Active Metal Brazing (AMB), Mo-Mn excels for large/complex geometries. For deeper insight into the microstructure and seal strength relationships in this classic process, see this peer-reviewed study: Microstructure and seal strength relation in the Molybdenum-Manganese glass metallization of alumina ceramics.
3. The 5 Performance Metrics That Actually Determine Reliability
Post-metallization, the part must balance ceramic insulation with metal-like joinability. Engineers focus on these:
- Hermeticity:Helium leak rate ≤1×10⁻¹⁰ to 10⁻¹² mbar·L/s (mass spectrometer standard)
- Adhesion: ≥20 MPa (shear test); military specs often ≥35 MPa
- CTE Gradient Matching: Al₂O₃ (~7-8 ppm/°C) → Mo → Ni → braze alloy to prevent thermal cycling cracks
- High-Frequency Loss: Tan δ <0.0002 @10 GHz (ideal for 77/79 GHz automotive radar)
- Thermal Cycling Endurance: -55°C to +350°C, 50,000 cycles without failure
Performance Impact Table (from real production data):
| Metric | Typical Value | Failure Risk & Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Leak Rate | 5×10⁻¹² mbar·L/s | Paste non-uniformity → add ultrasonic inspection |
| Thermal Cycling | 400 W/mm² power density | CTE mismatch → gradient layers or composite braze |
| Adhesion | 25-40 MPa | Surface contamination → rigorous plasma clean |
Substrate factors like porosity and glass phase content significantly influence these outcomes—detailed in this research: Influence of ceramic substrate porosity and glass phase content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of metallized ceramics via an activated Mo-Mn method.
4. Real-World Applications of Metallized Alumina Ceramic
- Vacuum Electronics – X-ray tubes, vacuum interrupters, microwave tube feedthroughs (hermeticity + high voltage)
- Power Electronics – IGBT/SiC module substrates, HVDC bushings (high thermal conductivity + insulation)
- Medical – MRI RF coils, implantable device housings (biocompatibility + long-term stability)
- Aerospace – Plasma thrusters, radar antenna windows (extreme temperature swings)
- EV/New Energy – Fast-charging connectors, high-voltage sensors (miniaturization + reliability)
Case Study: A global power module supplier used our 99.5% metallized alumina discs (φ150 mm, flatness 0.002 mm) – passed 8,000-hour thermal cycling with leak rate consistently <10⁻¹¹ Pa·m³/s.
For a broader review of alumina-to-metal joining technologies (including Mo-Mn and emerging alternatives), refer to this comprehensive overview: Joining alumina to metals: Technologies, challenges, and future prospects for high-performance structures.
5.Conclusion & Next Steps
Master these 5 points, and you'll select and qualify metallized alumina ceramic suppliers with confidence – saving time and avoiding costly iterations.
At Meetcera, we've specialized in 99.5% high-purity alumina metallization for 15+ years, delivering 100,000+ vacuum/power components to Tier-1 global clients. We offer:
- Free sample testing (with adhesion + helium leak reports)
- Download: "Metallized Alumina Hermeticity & Reliability Whitepaper"
- Custom quote in 48 hours
Click below to get started – share your specs (size, purity, application), and we'll match the optimal solution!