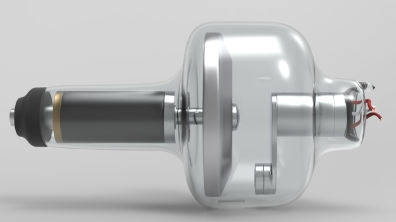
Comparing Different X-Ray Tube Materials: Ceramic vs. Glass vs. Metal-Ceramic
X-ray tubes are vital components. They power medical imaging systems. Material selection is paramount. It significantly affects performance. Durability and image quality are key. This article compares ceramic, glass, and metal-ceramic X-ray tubes. We will explore their strengths. We will also look at their weaknesses. This helps make informed decisions. Get ready to dive into the material details.
1. What Problems Do X-Ray Tube Materials Face?
Why is material choice so critical for X-ray tubes?
X-ray tubes operate under extreme conditions. They experience high temperatures and voltages. Material choice impacts heat dissipation. Vacuum maintenance is also crucial. Lifespan and image quality rely on it. Material must also resist chemical degradation.
Material choice is undoubtedly critical. It ensures long-term reliability. It also optimizes image quality.
What are the consequences of X-Ray Tube failure?
Tube failure causes downtime. This disrupts medical procedures. Poor heat dissipation leads to overheating. Vacuum leaks shorten tube life. Material degradation blurs image quality. Unexpected failures can be costly.
X-Ray Tube failures can severely disrupt operations. They lead to increased costs. They also delay critical diagnoses.
How do different materials address these challenges?
Ceramic offers high thermal resistance. Glass is cost-effective, but less durable. Metal-ceramic balances both aspects. Each material provides different solutions. Newer materials like composite are also emerging. Nano-materials boost performance.
Different materials offer a range of solutions. They tackle specific challenges effectively. The choice depends on application.
2. Ceramic X-Ray Tubes: Are They the Optimal Choice?
What sets ceramic X-ray tubes1 apart from other types?
Ceramic tubes have excellent thermal stability. They endure very high temperatures. They provide superior electrical insulation. This makes them ideal for high-power applications. They are used in advanced imaging systems. Their robust design extends lifespan.
Ceramic X-Ray Tubes exhibit exceptional thermal properties. They are the best for demanding applications.
How effectively do ceramic tubes manage intense heat loads?
Ceramic materials dissipate heat efficiently. This prevents tube overheating. It prolongs the tube's operational life. It ensures consistent performance. Even during prolonged, intensive use, the heat is managed well. They handle rapid temperature cycling effectively.
Ceramic tubes effectively manage extreme heat loads. They ensure stable operation. This leads to a prolonged lifespan.
Are there any drawbacks associated with using ceramic tubes in X-ray systems?
Ceramic tubes typically cost more. Manufacturing processes are complex. They might not be necessary for all applications. A cost-benefit analysis is essential. The high initial cost can be a barrier.
Ceramic tubes may have a higher upfront cost. Their long-term advantages often justify the investment.
3. Glass X-Ray Tubes: Are They Still Relevant?
What are the primary advantages of using glass X-ray tubes2?
Glass X-ray tubes are extremely cost-effective. They are relatively easy to manufacture. They are well-suited for low-power applications. They offer accessibility for basic imaging services. Their simplicity can aid in servicing.
Glass X-Ray Tubes are affordable and easy to produce. They remain useful for specific low-demand applications.
In which specific scenarios are glass tubes the preferred choice?
Glass tubes are preferred when budget is a major concern. They work well for low-intensity X-ray systems. This includes veterinary medicine clinics. They are suitable for basic educational purposes. They are also found in portable X-ray units.
Glass tubes are preferred in budget-conscious settings. They are adequate for lower-intensity needs.
What are the key limitations that come with using glass tubes?
Glass tubes offer lower heat resistance. They are more prone to cracking. They have shorter lifespans than ceramic tubes. They are not suitable for high-demand environments. They are also susceptible to thermal shock.
Glass tubes do have significant limitations. Their lower heat resistance is a major drawback.
4. Metal-Ceramic X-Ray Tubes: A Balanced Approach?
What key characteristics define metal-ceramic X-ray tubes3?
Metal-ceramic tubes combine material strengths. They offer good thermal dissipation capabilities. They provide enhanced mechanical strength. This translates into longer operational lifespan4s. They also improve the tube's robustness.
Metal-ceramic tubes offer a well-rounded solution. They combine the best aspects of both materials.
How do metal-ceramic tubes effectively balance cost and overall performance?
Metal-ceramic tubes cost more than glass options. However, they are more affordable than ceramic. They strike a good balance. This makes them a cost-effective option. Their versatility adds value.
Metal-ceramic tubes strike a fine balance. They offer good value for the investment.
In what typical applications are metal-ceramic tubes the ideal choice?
Metal-ceramic tubes work well for general radiography. They are beneficial in fluoroscopy procedures. They also fit in mid-range CT scanners. They cover broader medical imaging requirements. They are adaptable to various needs.
Metal-ceramic tubes are suitable for many common applications. They provide a versatile option.
5. X-Ray Tube Material Parameter Comparison
| Parameter | Ceramic | Glass | Metal-Ceramic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (20-30 W/mK) | Low (1-2 W/mK) | Moderate (10-15 W/mK) |
| Electrical Resistivity | High (>10^12 Ω·m) | Moderate (10^8 - 10^10 Ω·m) | High (>10^10 Ω·m) |
| Max. Operating Temperature | Up to 1200°C | Up to 400°C | Up to 800°C |
| Mechanical Strength | High (200-300 MPa) | Low (50-70 MPa) | Moderate (100-200 MPa) |
| Vacuum Tightness | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Cost (Relative) | High | Low | Moderate |
| Radiation Resistance | Good | Moderate | Good |
| Typical Lifespan | Long (5,000-10,000 hours) | Short (1,000-3,000 hours) | Medium (3,000-7,000 hours) |
This table provides detailed overview. It compares key parameters. It helps in informed decision-making. Each material shows unique properties. Match them with your needs.
6. Which X-Ray Tube Material Should You Choose?
| Feature | Ceramic | Glass | Metal-Ceramic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heat Resistance | Excellent | Low | Good |
| Cost | High | Low | Moderate |
| Lifespan | Long | Short | Medium |
| Application | High-power CT, Angiography | Basic X-ray, Veterinary | General Radiography |
| Mechanical Strength | High | Low | Moderate |
| Insulation | Excellent | Moderate | Good |
| Image Quality | Superior | Basic | Enhanced |
Choosing depends on your specific needs. Think about budget, power and tube lifespan. Ceramic is best for high-demand tasks. Glass fits basic, low-cost environments. Metal-ceramic is a balanced choice.
7. Future Trends in X-Ray Tube Materials
What innovations can we anticipate in X-ray tube materials?
Future may bring composite materials. Nanomaterials also will play a role. Advanced cooling tech will improve perfromance. Focus is on longer lifespan and better efficiency.
Advanced materials are being researched. They aim for enhanced performance. The future looks promising.
How will these changes affect medical imaging?
New materials could enable higher resolution. They may reduce radiation exposure. Faster scan times are also possible. Diagnosis will become more precise and safe.
These changes will revolutionize medical imaging. They will improve patient outcomes.
8. Conclusion
Selecting the right X-ray tube material is vital. Consider ceramic, glass, or metal-ceramic. Each has its unique advantages. Match the material to your specific needs. The right choice ensures great performance. It also maximizes equipment lifespan. This optimizes your overall investment.
Find out why ceramic X-ray tubes are preferred for high-power applications and their unique benefits. ↩
Explore the cost-effectiveness and applications of glass X-ray tubes in medical imaging. ↩
Learn about the balanced advantages of metal-ceramic X-ray tubes in various medical imaging scenarios. ↩
Learn effective strategies to maximize the operational lifespan of X-ray tubes in medical settings. ↩