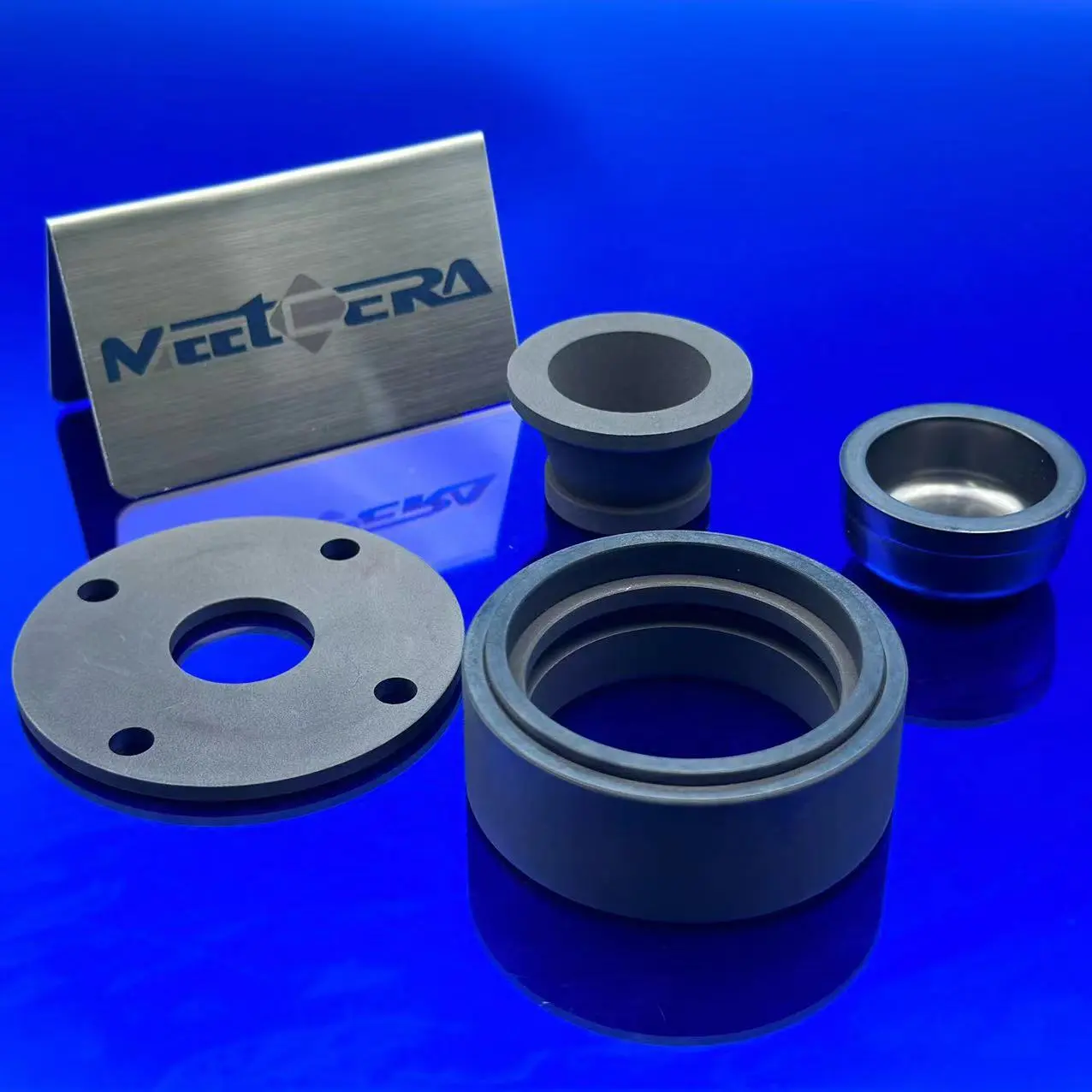
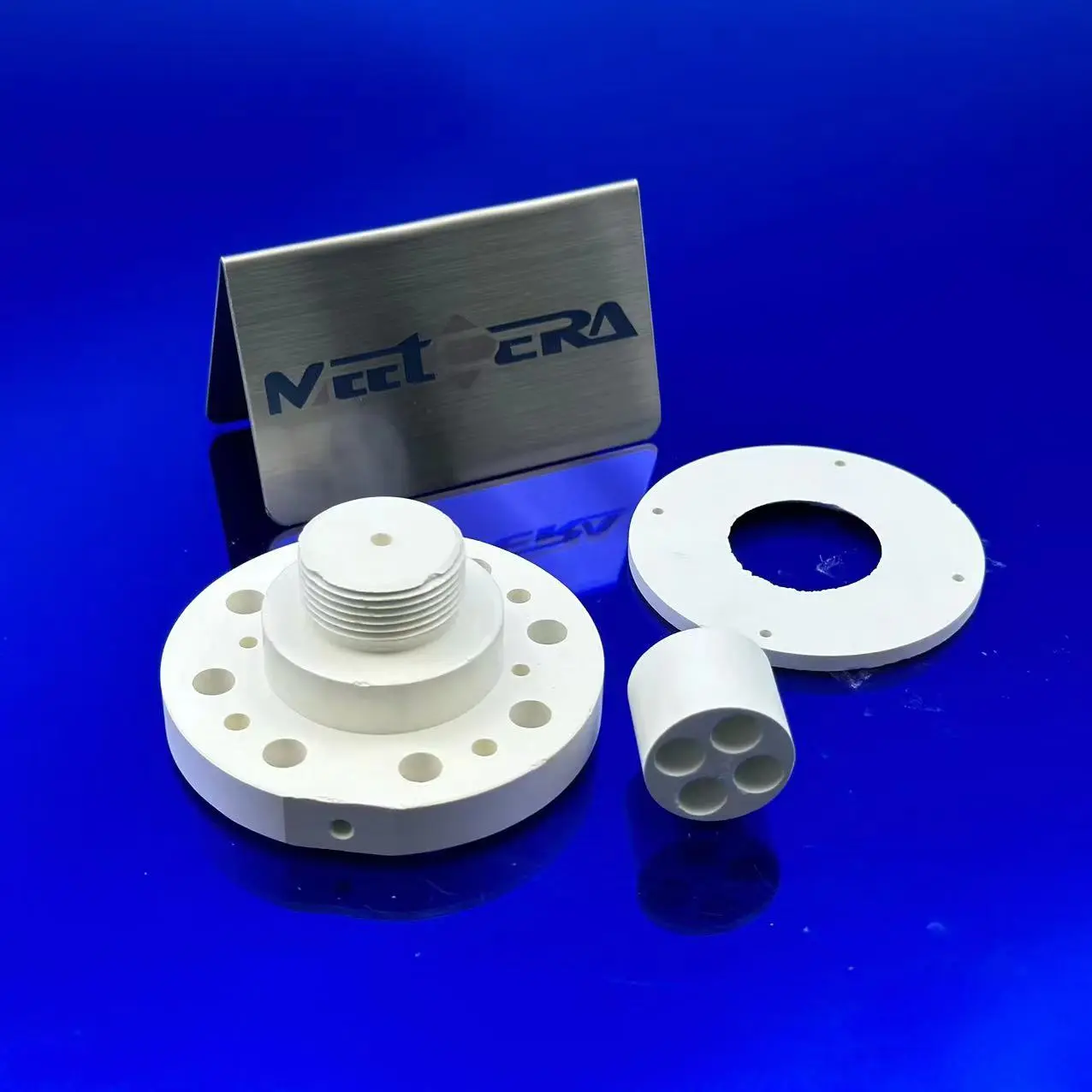
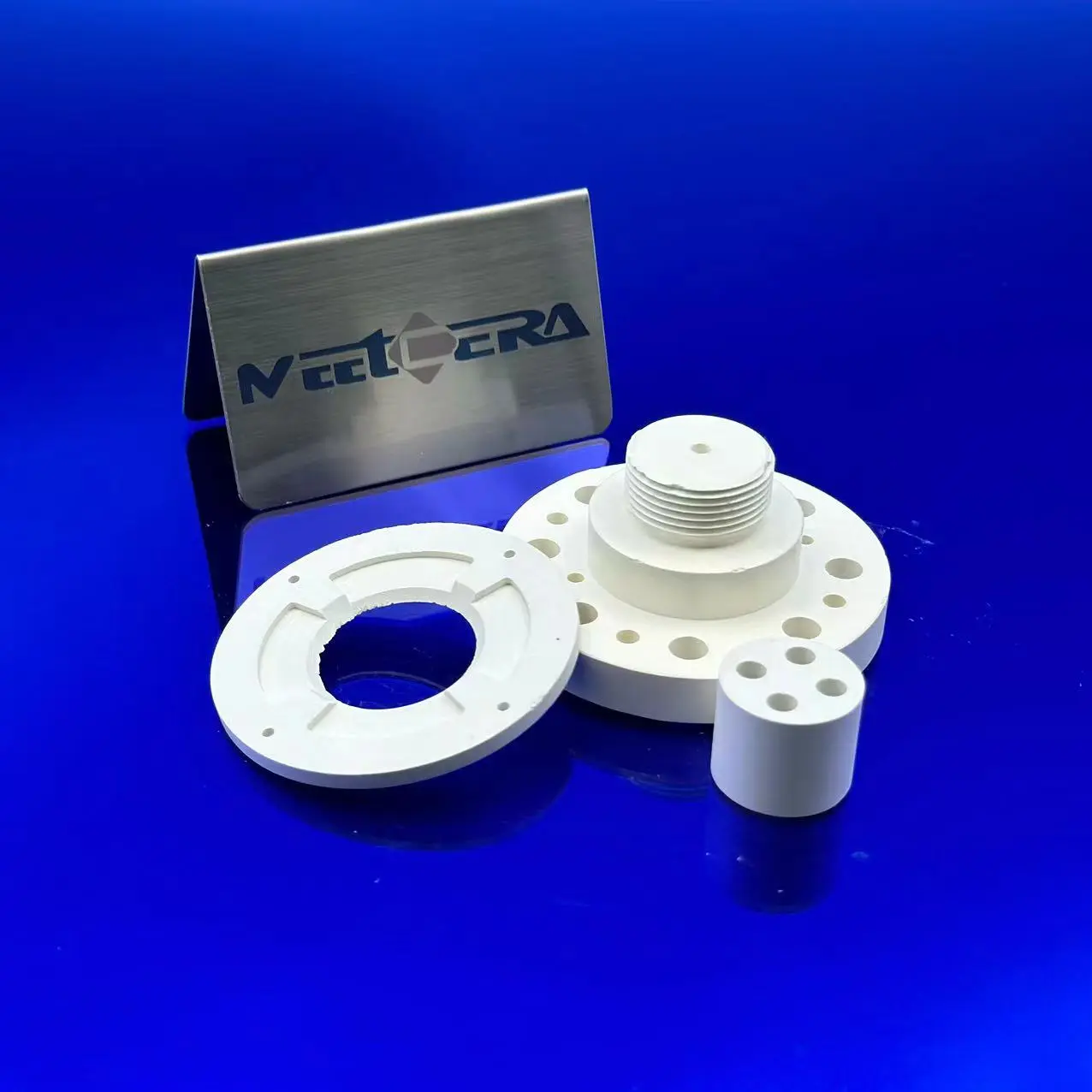
Boron Nitride Ceramic Parts
Hot-Pressed Boron Nitride (HPBN), often called "white graphite," is a high-purity, machinable ceramic sintered from hexagonal boron nitride (hBN). It combines graphite-like lubricity and easy machining with excellent high-temperature stability (up to 2100°C in inert/vacuum), electrical insulation, non-wetting by molten metals, and strong chemical inertness — making it ideal for extreme environments in semiconductors, high-temp melting, and vacuum furnaces.
Key Highlights
- Ultra-High Temperature Stability: Up to 2100°C in vacuum/inert atmospheres; 900–1000°C long-term in air
- Non-Wetting by Molten Metals: Zero adhesion with molten iron, steel, aluminum, copper, silicon, precious metals
- Exceptionally Machinable: Low hardness (Mohs 1–2), easily machined with standard carbide tools to ±0.01 mm precision
- Balanced Thermal & Electrical Performance: Thermal conductivity 20–60 W/m·K + dielectric strength >40–100 kV/mm
- High Chemical Inertness: Resistant to acids, alkalis, molten salts, plasma erosion
- Lightweight & Thermal Shock Resistant: Density ≈1.9–2.1 g/cm³
Typical Specifications
- Semiconductor / Photovoltaics: Diffusion boats, PVD/CVD parts, crystal growth crucibles
- High-Temperature Melting: Crucibles/nozzles for precious metals, rare earths, alloys
- Vacuum / Atmosphere Furnaces: Heater insulators, thermocouple tubes
- Power Electronics: High-temp insulating substrates, heat sinks
- Others: Plasma nozzles, nuclear components
FAQ
Q1: What is the main advantage of HPBN over alumina or zirconia ceramics?
A: Superior high-temperature stability (2100°C inert), non-wetting by molten metals, and easy machinability — unlike most oxides.
Q2: Can HPBN be machined on regular lathes?
A: Yes — low hardness allows standard carbide tools and tight tolerances (±0.01 mm) without diamond tooling.
Q3: What is the practical temperature limit in air vs. vacuum?
A: Air: ≤900–1000°C long-term. Vacuum/inert: 2000°C+ reliably