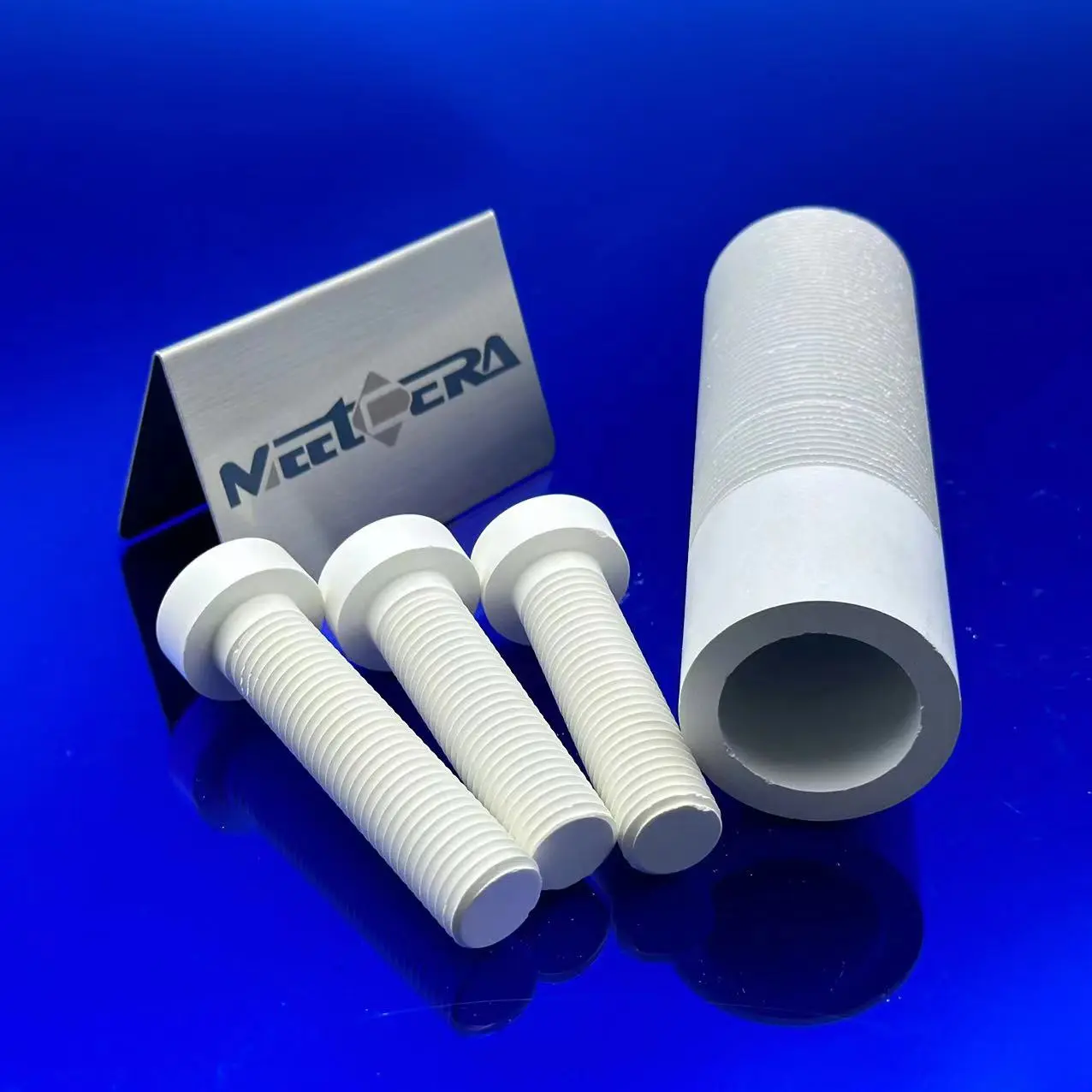
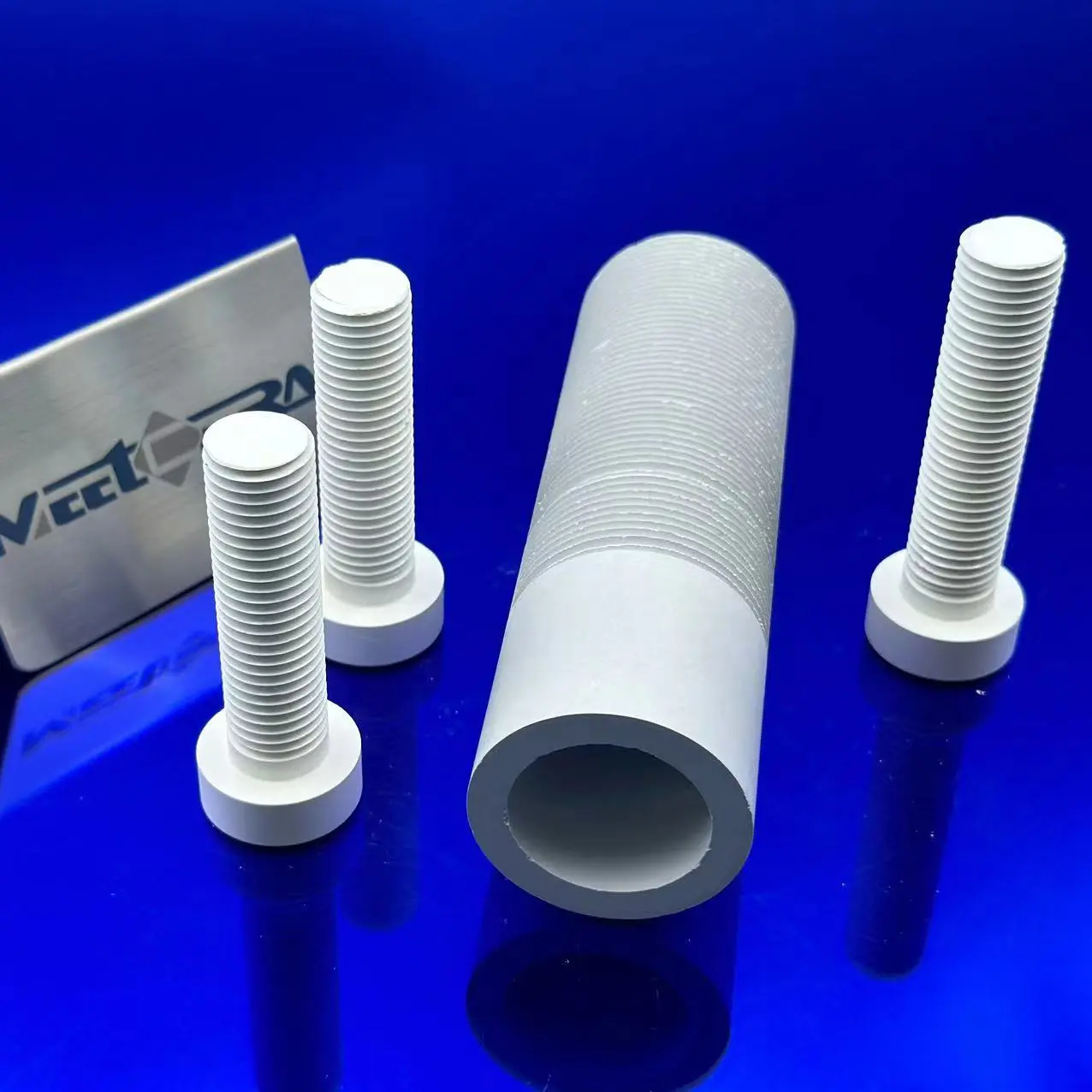
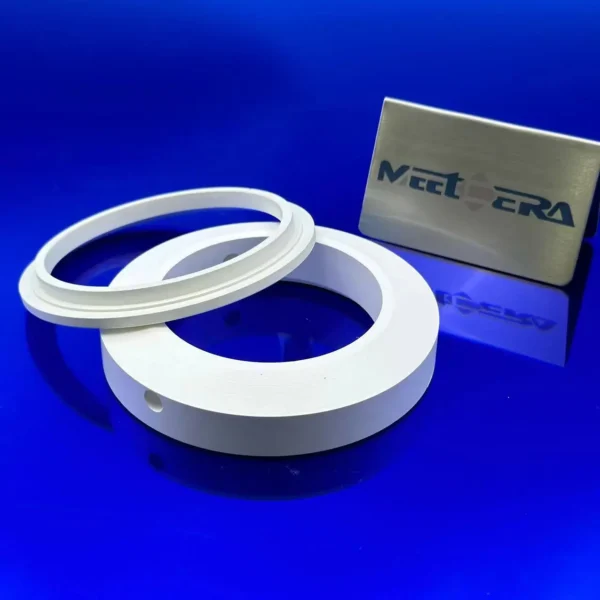
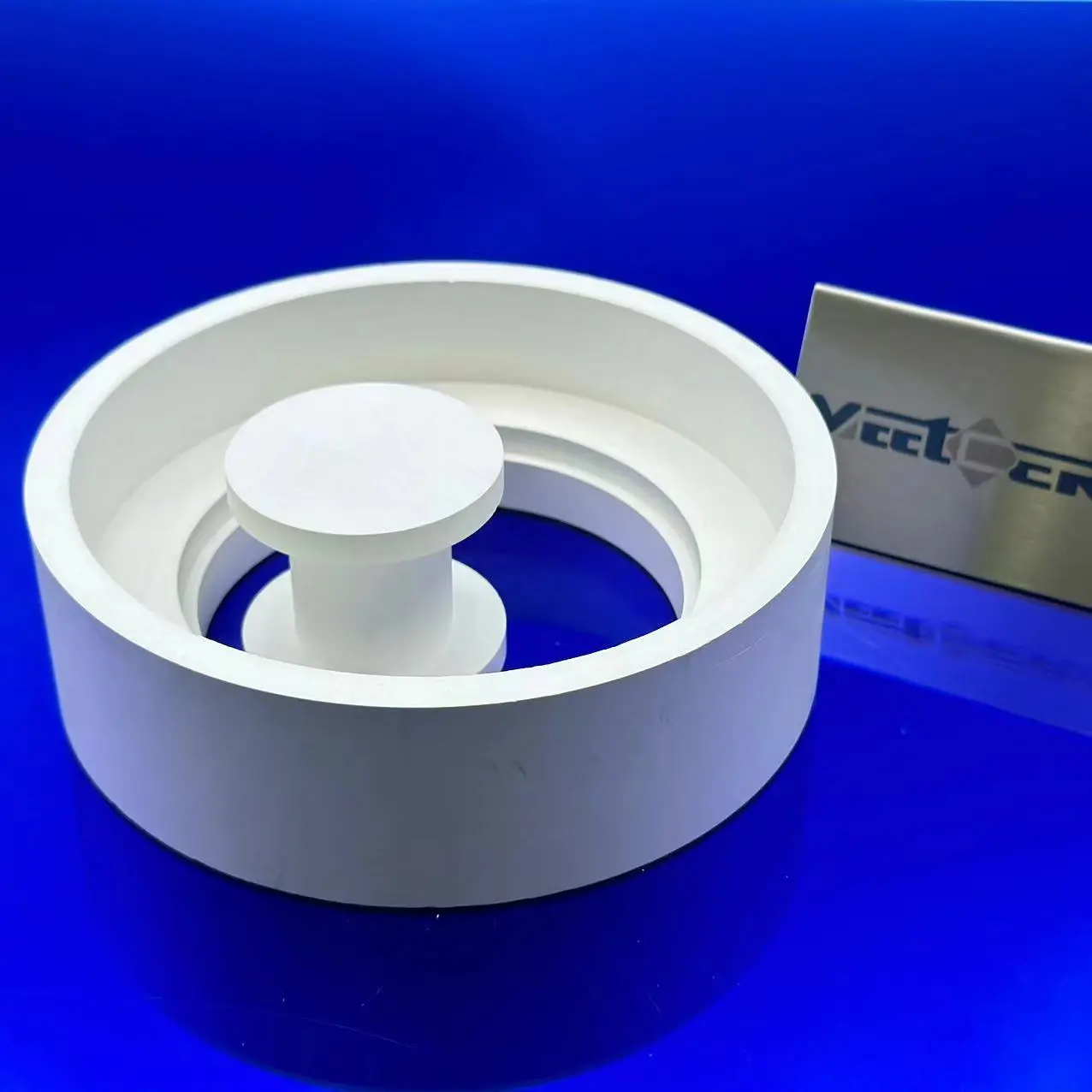
Boron nitride Parts
HPBN is made using a hot pressing process from densification of powder to a smooth white solid. It is hexagonal and a unique combination of chemical, electrical, mechanical and thermal properties, making it suitable for a wide range of high performance industrial applications.
Material Properties:
* High thermal conductivity
* Excellent thermal shock resistance
* Low thermal expansion
* Exceptional heat resistance
* Good Chemical Inertness
* High electrical resistance
* Low dielectric constant and loss tangent
* High volume resistivity
* Excellent machinability
Applications:
2. Vacuum melting crucibles
3. CVD crucibles
4. Microcircuit packaging
5. Sputtering targets
6. High precision sealing, brazing, and metallizing fixtures
7. Microwave tubes
8. Horizontal caster break rings
9. Low friction seals
10. Plasma arc insulators
11. High temperature furnace fixtures and supports
FAQ
Q1: What is the main advantage of HPBN over alumina or zirconia ceramics?
A: Superior high-temperature stability (2100°C inert), non-wetting by molten metals, and easy machinability — unlike most oxides.
Q2: Can HPBN be machined on regular lathes?
A: Yes — low hardness allows standard carbide tools and tight tolerances (±0.01 mm) without diamond tooling.
Q3: What is the practical temperature limit in air vs. vacuum?
A: Air: ≤900–1000°C long-term. Vacuum/inert: 2000°C+ reliably