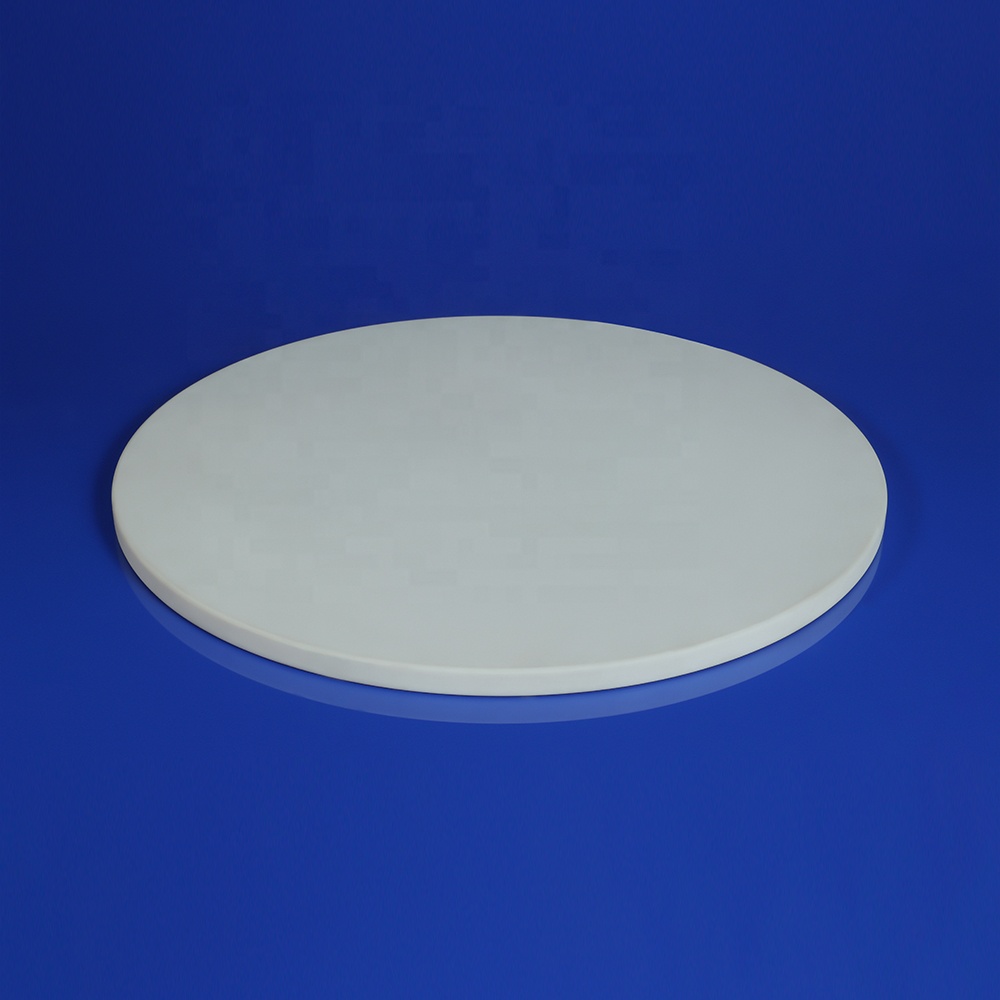
Zirconia Ceramic Sheet
Zirconia ceramic sheets are made from high-purity ultra-fine zirconia powder (ZrO₂ ≥ 94–99%), formed by isostatic pressing or dry pressing, followed by high-temperature precision sintering, and then finished with mirror polishing, precision grinding, chamfering, and other fine processing. Primarily yttria-stabilized zirconia (Y-TZP / YSZ), it combines extremely high toughness, hardness, and excellent environmental stability, making it one of the most balanced ceramic materials for modern high-end applications.
Key Features:
- Ultra-high toughness — Fracture toughness 6.5–9 MPa·m¹/², known as “ceramic steel”, excellent impact resistance, resistant to shattering and chipping.
- Extremely high hardness & wear resistance — Vickers hardness HV 1100–1350, highly scratch-resistant surface, service life far exceeds ordinary ceramics.
- Outstanding corrosion resistance & high-temperature stability — Resistant to strong acids/alkalis, seawater, molten metals; long-term use at 800–1000℃; low thermal conductivity (2–3 W/m·K).
- Electrical insulation & no signal shielding — Excellent insulating properties, low loss at high frequencies, ideal for 5G and other high-frequency electronic devices.
Typical Application Scenarios:
- High-end consumer electronics — 5G structural support sheets, camera spacer plates, fingerprint/face recognition windows
- Precision machinery — Wear-resistant gaskets, guide rails, valve plates, seals, cutting blade carriers
- Medical & biotechnology — Dental substrates, beauty device contact plates, minimally invasive surgical auxiliary components
- Semiconductor & vacuum — Wafer carrier sheets, plasma etching barrier plates, insulating heat-dissipation sheets
- Aerospace & scientific research — High-temperature insulation sheets, oxygen sensor elements, corrosion test substrates
Customization Capabilities Thickness: starting from 0.05 mm Maximum size: 150×150 mm or Φ150 mm Processing: CNC cutting, laser engraving, metallization, mirror/matte polishing Precision: tolerance ±0.001 mm, surface roughness Ra ≤0.05–0.1 μm Supports small-batch prototyping to large-scale production.
FAQs
Q1: What is the biggest difference between zirconia ceramic sheets and ordinary alumina ceramic sheets?
A: The fracture toughness of zirconia is 2–3 times that of alumina (6.5–9 vs 3–5 MPa·m¹/²), meaning it is far more impact-resistant, much less prone to shattering or chipping — often called “the least brittle ceramic”. It is ideal for applications requiring drop resistance and collision tolerance, while alumina is more brittle but lower in cost.
Q2: Will this ceramic sheet break if dropped on the floor? How much impact can it withstand?
A: Thanks to the transformation toughening mechanism, it generally will not shatter or suffer serious chipping when dropped from typical desk height (about 1 meter) — significantly more drop-resistant than ordinary ceramics. However, it is still a ceramic material — avoid extreme heavy impacts (e.g., hammer blows) or sharp-edge collisions, which may cause microcracks. Its actual impact resistance far exceeds alumina and approaches the toughness of some metals.