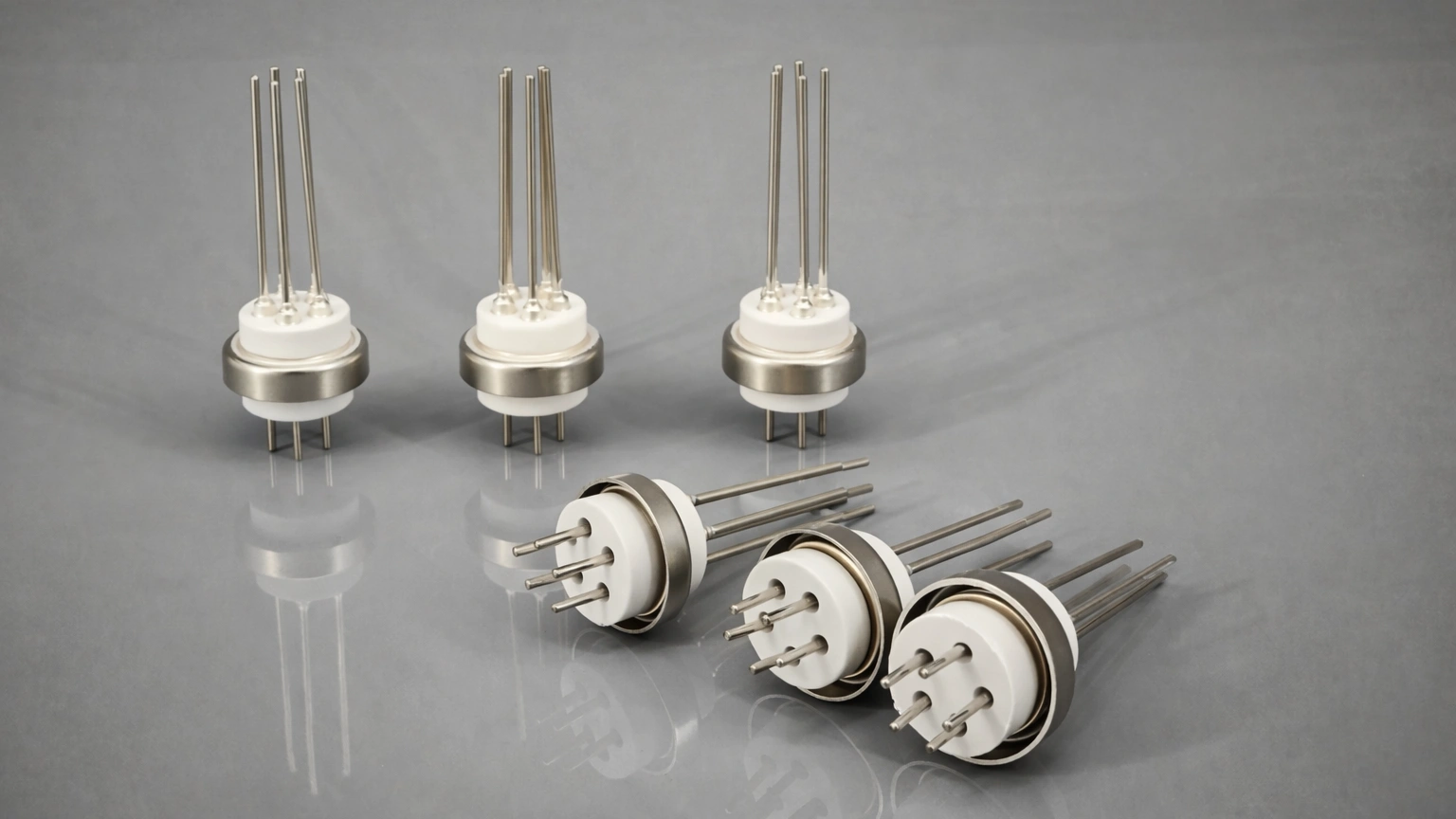
What Are the Different Types of Vacuum Feedthroughs?
Vacuum feedthroughs are critical components in high-vacuum (HV) and ultra-high vacuum (UHV) systems. They allow the transfer of electricity, fluids, gases, or mechanical motion from the atmospheric side to the vacuum side while maintaining a hermetic seal.
Understanding the different types of vacuum feedthroughs helps you select the right solution for applications such as semiconductor manufacturing, thin-film deposition, research chambers, and cryogenic systems.
This guide explores the main categories of vacuum feedthroughs and their subtypes.
1. Electrical Feedthroughs
Electrical feedthroughs transmit electrical power or signals into a vacuum environment. They vary by voltage, current, and signal type.
| Subtype | Typical Applications | Features |
|---|---|---|
| High-Current Power Feedthroughs (Learn more) | Deposition sources, sputtering targets, substrate heating | Low voltage (<50 V) but high current (hundreds–thousands of amps); optional water cooling for high thermal loads |
| Thermocouple Feedthroughs (Learn more) | Temperature monitoring in vacuum chambers | Accurate temperature measurement; maintains vacuum integrity |
| Multipin Feedthroughs (Learn more) | Instrumentation, sensors, control signals | Multiple electrical connections in a single unit |
| Coaxial Feedthroughs | High-frequency signal transmission | Shielded conductors; minimal interference |
| RF Feedthroughs | RF plasma, deposition systems | Optimized for radio-frequency power; low signal loss |
2. Fluid and Gas Feedthroughs
Fluid and gas feedthroughs allow liquids or gases into a vacuum chamber for cooling, purging, or process gas delivery.
| Subtype | Applications | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Fluid/Gas Feedthroughs (Learn more) | General cooling or gas delivery | Stainless steel tubing, VCR or Swagelok fittings, high bakeout capability |
| Cryogenic Feedthroughs | Liquid nitrogen (LN₂), liquid helium (LHe) | Thermal insulation shields to prevent condensation; suitable for UHV cryogenic applications |
3. Rotary Motion Feedthroughs
Rotary feedthroughs transmit rotational motion into the vacuum chamber. Common uses include sample manipulation, beam steering, or rotating sputtering targets.
| Seal Type | Applications | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Elastomer-Sealed Rotary Feedthroughs | Lower RPM applications | O-ring seals; serviceable; cost-effective; good torque at moderate speeds |
| Ferro-Sealed (Ferrofluid) Rotary Feedthroughs | High RPM / high torque | Magnetic ferrofluid seals; minimal particles; ideal for UHV and clean environments |
4. Transition Feedthroughs
Transition feedthroughs, or baseplate feedthroughs, provide adaptable interfaces for vacuum chamber ports.
| Type | Applications | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Flange-Based Transition Feedthroughs (Learn more) | Mounting gauges, sensors, or additional components | Compatible with standard flanges: ConFlat (CF), ISO-QF (KF) |
| Fitting-Based Transition Feedthroughs | Flexible system connections | Female NPT threads, quick disconnects, blank plugs |
5. Key Considerations for Choosing Vacuum Feedthroughs
When selecting a vacuum feedthrough, consider:
- Type of transfer (electrical, fluid/gas, motion, or transition)
- Vacuum level (HV vs. UHV)
- Operating temperature and bakeout requirements
- Electrical current and voltage ratings
- Material compatibility
- Flange and connection standards
Choosing the right feedthrough ensures system efficiency, reliability, and leak-free operation. For specialized applications, consult with vacuum system experts.

6. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is the main purpose of a vacuum feedthrough?
A: To maintain a hermetic seal while allowing power, signals, fluids, gases, or motion between atmospheric and vacuum environments.
Q: Can vacuum feedthroughs be used in cryogenic applications?
A: Yes. Specialized cryogenic feedthroughs support low-temperature fluids like liquid nitrogen, with insulation to minimize heat leakage.
7. Conclusion & Next Steps
Selecting the right vacuum feedthrough ensures reliable and efficient operation of your vacuum system. Explore high-quality feedthroughs tailored to your applications and consult qualified suppliers for:
- Custom solutions
- Detailed specifications
- Technical support for HV, UHV, or cryogenic systems
Optimize your vacuum system today by choosing the right feedthrough technology for your application.