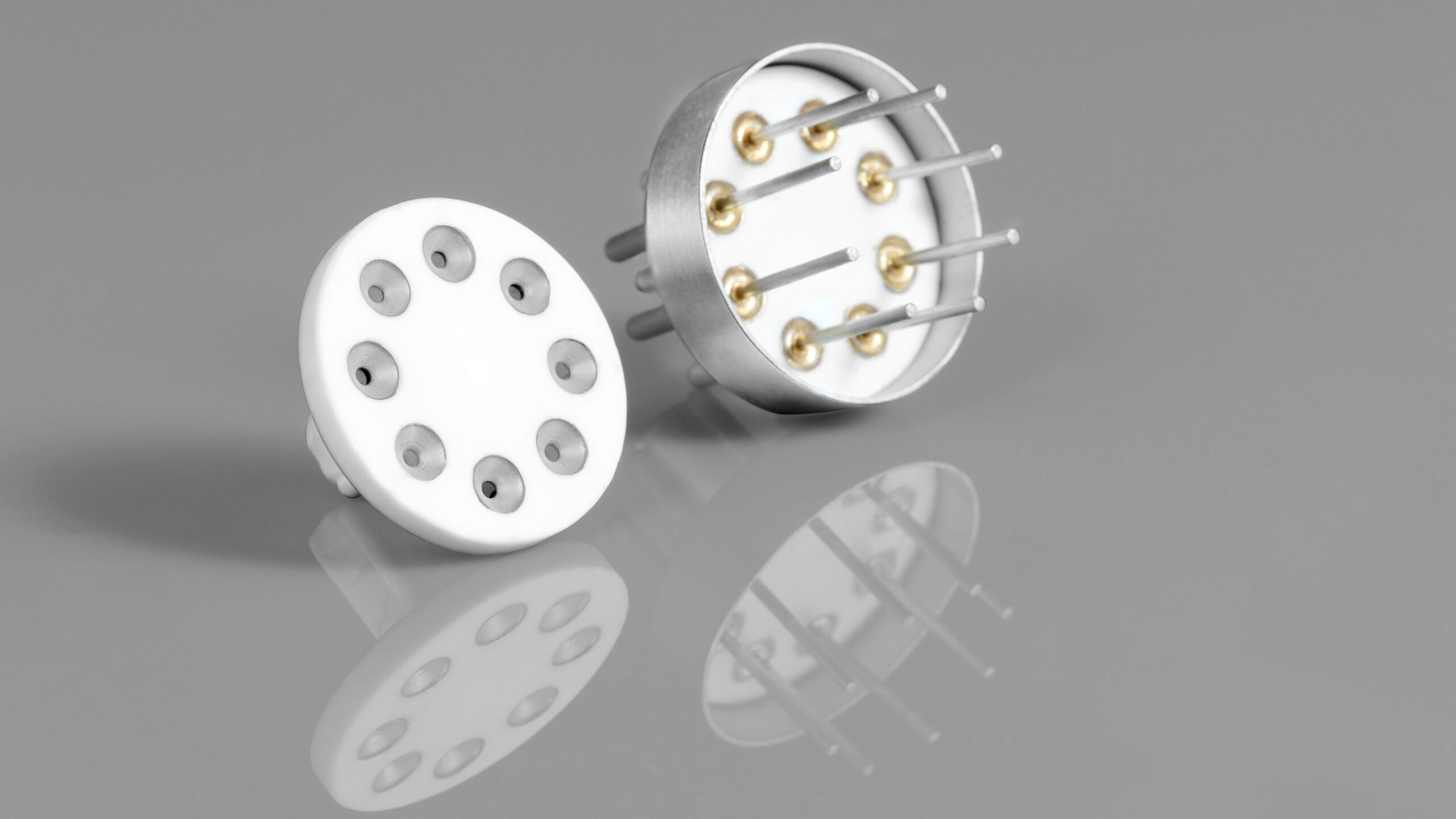
What is a Vacuum Feedthrough?
Imagine a vacuum environment (such as a high-energy particle accelerator or a semiconductor deposition chamber) that must remain absolutely pristine and isolated. How can you introduce power, motion, or fluid into this chamber without compromising its integrity?
The answer lies in the Vacuum Feedthrough1.
- Definition: A vacuum feedthrough is a precisely engineered component that allows energy, matter, or mechanical motion to pass through the wall of a vacuum vessel while maintaining an absolute hermetic seal at the interface, ensuring the vacuum level is not degraded. They are the heart component of all advanced vacuum systems.
This article will delve into the types and working principles of vacuum feedthroughs and highlight how metallized ceramic technology2 provides a superior solution for your critical applications.
1. Working Principle and Core Role of Vacuum Feedthroughs
Before diving into the specific types of vacuum feedthroughs, we must first understand their most critical responsibility: maintaining the integrity of the vacuum. This involves hermeticity, material selection, and endurance against extreme conditions.
1.1 The Essential Function: The Hermetic Interface
A vacuum feedthrough must possess an extremely high degree of hermeticity (Hermetic Seal). In High Vacuum (HV) and especially Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) environments, even a minuscule leak can drastically reduce the vacuum level and cause system failure.
The key roles of a vacuum feedthrough are to provide a physical pathway while ensuring:
- Isolation: For electrical signals or power, the internal conductor must be electrically isolated from the external environment.
- Low Outgassing: The materials themselves must not release gases in a vacuum, which is essential for maintaining UHV.
- Environmental Resistance: The ability to withstand high-temperature bake-outs, significant thermal gradients, and high-pressure differentials.
1.2 Seal Technology and Material Selection
Since hermeticity is so crucial, the choice of sealing material is paramount. The performance of a feedthrough is dictated by its core sealing material. Traditional materials like elastomer O-rings (for HV environments) or glass-to-metal seals have limitations.
🥇 Our Advantage: Metallized Ceramic Sealing Technology
For applications requiring resilience to extreme conditions (e.g., high-temperature bake-out, $ > 350^\circ\text{C}$), high current, or high voltage (High Voltage), the metallized ceramic (Ceramic-to-Metal) seal is the gold standard.
- Superior Electrical Insulation: Ceramics have extremely high dielectric strength, allowing the safe transmission of power required by high voltage vacuum feedthroughs3.
- Thermal Stability: They maintain structural integrity and hermeticity during UHV bake-out procedures.
- Mechanical Strength: The precise matching of ceramic and metal ensures the seal remains reliable under severe thermal cycling.
2. Common Types and Applications of Vacuum Feedthroughs
Based on different functional requirements, Vacuum Feedthroughs are engineered into various types. Understanding these types will help you determine which feedthrough is best suited for your specific application.
Vacuum Feedthroughs are categorized based on the medium or function they transmit:
2.1 Vacuum Electrical Feedthrough
As the name implies, electrical feedthroughs are the most important channel for connecting external power and signals to the vacuum interior.
This is the most common category, used to introduce electrical current or signals into the vacuum chamber:
- Multi-pin Feedthroughs: For transmitting low-voltage signals and data.
- High Current Feedthroughs: Used for high-power applications like heaters or filaments.
- High Voltage Feedthrough: Specifically designed for applications like electron or ion sources that require voltages exceeding $ > 1 \text{kV}$. Our ceramic high voltage vacuum feedthroughs offer unparalleled insulation and reliability.
2.2 Vacuum Rotary Feedthrough and Mechanical Motion
Beyond transmitting energy, many vacuum processes require precise movement of internal components, which necessitates dedicated mechanical motion feedthroughs.
A vacuum rotary feedthrough allows external rotational motion (e.g., for driving manipulators, sample stages, or shutters) to be transferred into the chamber without breaking the vacuum.
- Working Principle: Often achieved via magnetic coupling (contactless, high cleanliness) or bellows sealing (physical barrier).
- Applications: Primarily used in vacuum manipulators, sample handling, and precise positioning systems.
2.3 Fluid, Optical, and Thermocouple Feedthroughs
In addition to electricity and mechanical motion, other key elements must be introduced into or extracted from the vacuum chamber, such as temperature measurement and coolants.
- Fluid Feedthroughs: Used for coolants, reaction gases, or liquids.
- Optical Feedthroughs: Used for fiber optics or laser beams, transmitting light signals through a transparent window.
- Thermocouple Feedthroughs: Transmit temperature measurement signals.
3. How to Select the Right Vacuum Feedthrough for Your Application
Selecting the correct feedthrough is the first step in ensuring system reliability. Here are the critical parameters you must consider during the selection process:
When selecting the most appropriate vacuum feedthrough, you must consider the following critical parameters:
| Parameter | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Level | UHV (Ultra-High Vacuum) environments must use low-outgassing, bakeable metallized ceramic or glass-to-metal seals. HV (High Vacuum) allows for more options. |
| Operating Conditions | Does it need to withstand high-temperature bake-out4? Are there high current or high voltage requirements? |
| Transmission Type | Determines whether you choose electrical, rotary, fluid, or optical feedthroughs5. |
| Flange Type | Common types include CF (UHV standard), ISO, and KF/NW flanges; must match the vacuum chamber. |
Conclusion
The vacuum feedthrough is the cornerstone of any successful high-technology vacuum system. They must be precise, reliable, and maintain hermeticity under extreme conditions.
Does your application need to withstand high pressure, high current, and Ultra-High Vacuum demands?
Our expertise lies exactly there. We specialize in manufacturing and customizing all types of vacuum feedthroughs based on metallized ceramic seals, with leading technology particularly in high voltage vacuum feedthrough and customized vacuum electrical feedthrough6 solutions.
💡 Your Next Step:
- Explore our High Voltage Vacuum Feedthrough product line to see how our ceramic technology can offer you superior performance.
- Contact our engineers for expert advice on the best solution for your specific application (e.g., a custom vacuum rotary feedthrough).
Understanding vacuum feedthroughs is essential for maintaining vacuum integrity in advanced systems. ↩
Discover how metallized ceramic technology enhances performance in extreme conditions. ↩
Explore the applications of high voltage feedthroughs in advanced vacuum systems. ↩
Understanding bake-out processes is crucial for maintaining vacuum integrity. ↩
Learn about optical feedthroughs for transmitting light signals in vacuum systems. ↩
Explore the role of electrical feedthroughs in connecting power to vacuum systems. ↩