X-ray Tube Types and Advanced Metallized Ceramic Solutions
In 2025, demand for X-ray tubes surges across medical CT, industrial NDT, and analytical instrumentation. Traditional glass-envelope designs are rapidly being replaced by metal ceramic X-ray tubes, driven by superior thermal performance, higher voltage capability (up to 320 kV), and 2–5× longer service life.
At the heart of this transition are metallized alumina ceramics, typically using Mo–Mn metallization, which enable reliable hermetic sealing, excellent high-voltage insulation, and robust ceramic-to-metal brazing—eliminating common failure modes such as cracking, arcing, and vacuum leakage.
Comparison of Major X-ray tube Types
| Tube Type | Typical Voltage | Focal Spot Size | Power / Duty Cycle | Key Strength | Main Ceramic Demand | Typical Lifespan Gain with Metal-Ceramic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Anode (Sealed) | 20–160 kV | 0.1–1 mm | Low–Medium | Cost-effective, compact | Vacuum seals, feedthroughs | +50–100% |
| Rotating Anode | 80–160+ kV | 0.3–1 mm | High / Continuous | High heat dissipation | High-dielectric insulators, thermal stability | +200–400% |
| Beryllium Window | 5–80 kV | 0.05–0.5 mm | Low–Medium | Soft X-ray transmission | Precision low-absorption window assemblies | Improved reliability in XRF |
| Microfocus / Nanofocus | 20–150 kV | <50 μm (down to 1 μm) | Medium | Ultra-high resolution | Precise field control, compact HV designs | Critical for <10 μm spot stability |
| End-Window | 10–80 kV | Small | Low | Max flux near sample | High-efficiency output seals | Enhanced analytical sensitivity |
| Open-Type (Transmission / Reflection) | Up to 300 kV | Variable | Research / High | Replaceable target | Durable brazed seals for UHV | Long-term lab stability |
1. Fixed Anode X-ray Tubes
Fixed anode tubes remain dominant in portable NDT, basic radiography, and security inspection (20–150 kV).
Challenge: Repeated thermal cycling and high electric fields often cause glass envelope cracking or seal degradation.
Modern solution: Metal envelopes combined with Metallized Alumina Ceramic Rings & Tubes provide:
- Hermetic sealing
- Superior insulation (>10¹⁴ Ω·cm)
- Brazing strength >150 MPa
- Helium leak rates <10⁻¹⁰ Pa·m³/s
Mo–Mn metallization with Ni/Au plating ensures long-term reliability.
2. Rotating Anode X-ray Tubes
Used in CT scanners, angiography, and high-resolution radiography, rotating anode tubes operate at >100 kV and high mA.
Key requirement: Exceptional dielectric strength and thermal shock resistance.
Advantage of metallized ceramics:
- High-purity alumina withstands >200 kV/mm
- Reduced arcing and partial discharge
- Tube lifetime extended from ~5,000 hours (glass) to 15,000–30,000+ hours
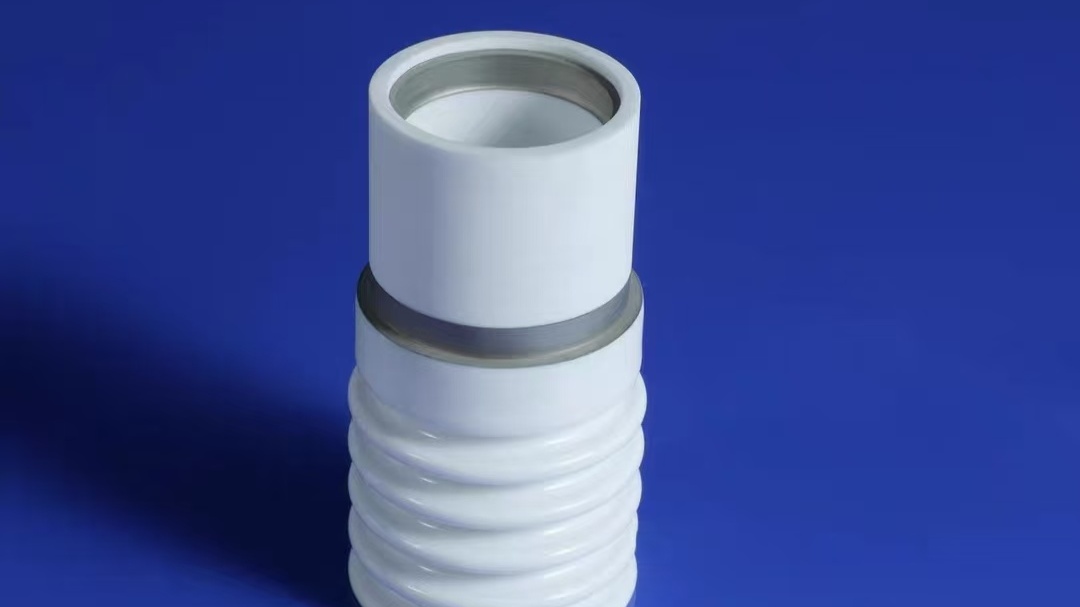

3. Beryllium Window & End-Window Tubes
Critical for XRF elemental analysis and material characterization, where thin Be windows minimize soft X-ray absorption.
Role of ceramics:
- Precision metallized end-window components maintain UHV integrity
- Support high photon flux and long-term alignment stability
Meetcera’s tight-tolerance Mo–Mn metallized alumina enables sub-micron alignment accuracy.
4. Microfocus X-ray Tubes
Microfocus and nanofocus tubes (spot sizes <50 μm, some <5 μm) are essential for:
- Semiconductor inspection
- Electronics failure analysis
- Micro-CT
Key requirement:
- Extremely stable electric field
- Compact, high-voltage insulation
Metallized ceramic components provide precise field control and minimize off-focus radiation.
5. High-Voltage Power Supply Configurations & Ceramic Insulation Needs
Common HV configurations include:
Anode Grounded
Negative HV on cathode; excellent heat dissipation; common up to 160 kVCathode Grounded
Positive HV on anode; simpler filament driveBipolar
±160 kV (total 320 kV); highest power density
Metallized alumina feedthroughs and insulators are essential across all configurations.
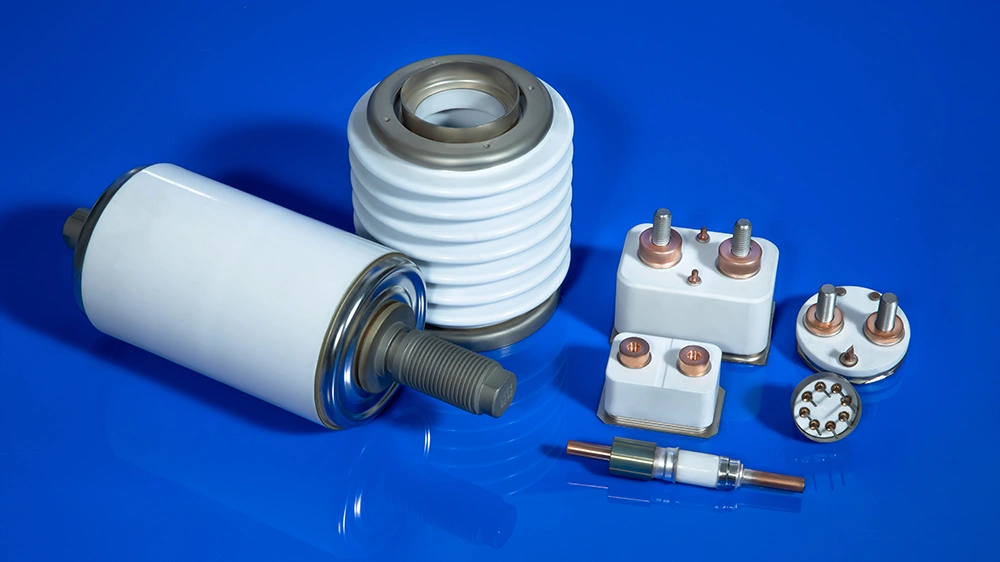

6.How to Select Metallized Ceramic Components for Your X-ray Tube
| Use this checklist to evaluate your requirements: | Criteria | Checked |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Operating voltage & dielectric strength Up to 320 kV; confirm required kV/mm margin | ☐ | |
| 2. Thermal load & cycling frequency Continuous rotating anode vs. intermittent fixed anode | ☐ | |
| 3. Required vacuum level UHV <10⁻⁸ Pa for long-term stability | ☐ | |
| 4. Brazing compatibility AgCu, AuNi, or other fillers with Mo–Mn layer | ☐ | |
| 5. Compliance & certifications IEC 60601, ISO 9001, ISO 13485 | ☐ |
Case example
An industrial CT OEM achieved >25,000 hours of continuous operation without vacuum degradation using Meetcera metallized insulator rings (internal accelerated life testing, 2025).
7.Why Partner with Meetcera for Metallized Ceramic Solutions?
With decades of focus on high-voltage vacuum assemblies, Meetcera delivers:
- Advanced Mo–Mn and active metallization systems
- Leak-tight brazed joints (He leak <10⁻¹⁰ mbar·L/s)
- Custom geometries: tubes, rings, discs, feedthroughs
- Full batch traceability and reliability testing
📩 Contact us at Meetcera for samples, CAD collaboration, or technical consultation.
8.FAQ
Q: Why are metal ceramic X-ray tubes replacing glass ones?
A: They provide superior thermal shock resistance, higher voltage capability (up to 320 kV), and 2–5× longer service life in demanding applications.
Q: What is Mo–Mn metallization and its main benefit?
A: Mo–Mn metallization creates a strong, hermetic interlayer on alumina, enabling reliable ceramic-to-metal brazing and high-reliability vacuum seals.
Need tailored metallized alumina components for your next X-ray source project?
Reach out today.